M-Port: An AI-Powered DID Platform based on Biometric Information (III)
M-Port: A DID Solution Based on the Matrix Mainnet and Biometrics
In response to the challenges DID is facing, Matrix has come up with the perfect solution.
Inspired by the separation of powers, Matrix has designed a Hybrid PoW consensus mechanism, which finds a perfect balance between security and performance. With a TPS of more than 10,000, M-Port will be safe and efficient to use.
In the meantime, based on its experience developing biometric wallets, Matrix has also designed a unique AI algorithm for finger vein scanning.

Finger vein verification provides the perfect solution for connecting the physical and the virtual worlds and will guarantee anonymity at the same time. Finger vein biometrics is unique for every person. It is not only an identity marker that everyone carries on their physical bodies but also something that governments and companies don’t collect.
The way M-Port works is as follows:
1. It connects real-world users through finger vein biometrics;
2. It uses blockchain to keep records and match finger vein data with users to whom the biometrics belongs;
3. It uses distributed storage to keep user data safe;
4. When apps connected to M-Port want to use such data, it grants them access through distributed computing.
To make all this come true, we need Matrix to provide the necessary infrastructure.
Matrix Provides the Best Infrastructure Available for M-Port
As a next-generation DID platform, M-Port will require solid infrastructure and cutting-edge tech support.
Matrix Mainnet: A High-Performance Ledger
This high-performance ledger is none other than blockchain, which is essentially a distributed bookkeeping technology. By involving multiple parties into the bookkeeping process, blockchain can guarantee trustability, reliability and immutability.
Why do we need a high-performance ledger? This is because when valuable data are transmitted from one point to another, we need a way to guarantee the reliability of this process without recourse to centralised institutions. This is where blockchain will shine. In order for people to adopt Web 3.0 on a large scale in the future, the development of a high-performance blockchain brooks no delay.
The Matrix Mainnet currently boasts a TPS of more than 10,000, ranking among the best public chains. In the early stage of Web 3.0, this concurrency will be more than enough to support the DID of the whole network. In the future, Matrix will continue to upgrade its hardware and technologies, building a solid foundation for M-Port.
MANTA—The Ultimate Distributed Computing Platform
DID requires a technology called trustless computation. It’s a solution that enables a group of untrusting participants to collaborate on solving the same problem without compromising the privacy of each.
Take the healthcare industry for example. Hospitals are forbidden by law to leak their patients’ personal information, let alone share it without permission or sell it for profit. Paradoxically, large quantities of patient data are necessary for medical research. This is where trustless computation comes to play. Through secure multi-party computation, participants can work together on calculating, categorising and analysing data without leaking anything that can be traced to its owners.
MANTA’s distributed computing is a perfect example of trustless computation. This, in combination with machine learning, will create endless possibilities for M-Port.
Matrix IPFS—Trustable Storage
Storage is at the core of DID’s data security. Up to now, trustable storage is mostly achieved through IPFS, which has the following characteristics:
1. Once loaded into storage, data are almost impossible to tamper with or delete
2. All data can be directly accessed. Whether it’s text, video or music stored in an IPFS network, they are all directly accessible through hash.
Matrix’s IPFS storage is an important part of the infrastructure of Web 3.0. It is responsible for storing Web 3.0’s content and access protocols. Just like the cloud storage services we are used to today, distributed storage will become the essential infrastructure for storing and distributing content in the future.
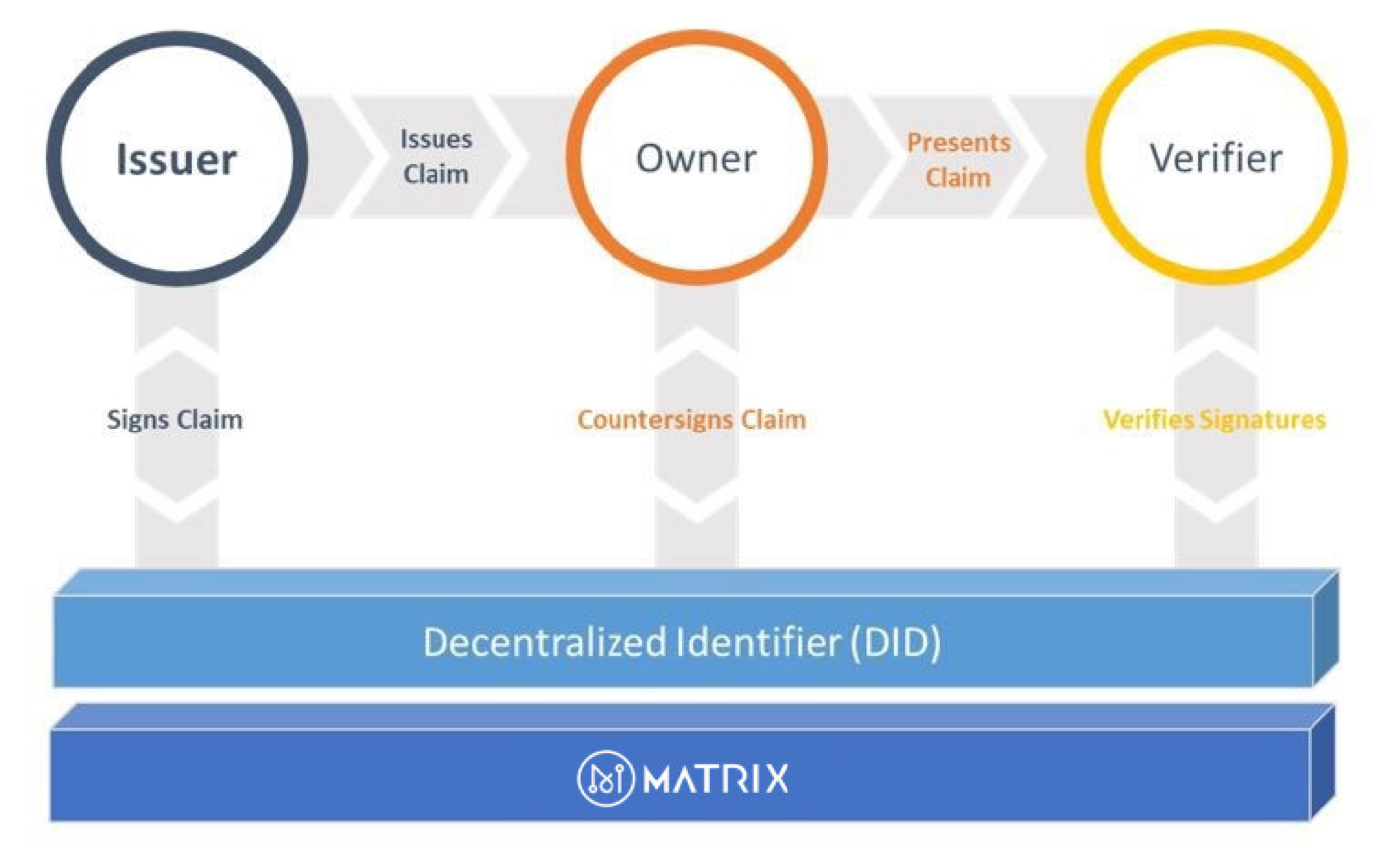
M-PORT’s Multi-Layer Structure
Layer 1: Standards and Identifiers
The mutual trust layer of M-Port consists of standards, identifiers and namespaces. It serves to ensure standardisation, transferability and co-operability, allowing developers and users from different networks to register and manage their decentralised identities.
Layer 2: Infrastructure
Infrastructure and proxy frameworks enable apps to communicate with one another. These solutions will apply to communication, storage and private key management scenarios.
Layer 3: Proofs
A biometric DID verification system can manage, update and exchange proofs. The function of this layer is to allow users to prove their DID ownership so that data can be transferred reliably and securely.
Layer 4: Apps, Wallets and Other Products
M-Port will provide complete ports and tools for developers to build decentralised apps and products. Users will directly benefit from the convenience and efficiency of Matrix-based services.

Last updated