MANTA—The Brain of Tomorrow’s Metaverse
Please read in conjunction with
https://www.matrix.io/blog/A_Brief_History_of_Metaverse_168.html
So what is the Metaverse?
Epic Games CEO Tim Sweeney believes that the Metaverse will become a real-time 3D medium with a completely fair economic system, one that people participate in on an unprecedented scale.
Roblox CEO David Baszucki believes that the Metaverse is a long-lasting, shared 3D virtual space, within which people take on their personalized avatars to participate in entertainment, work and creative activities.
Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg thinks of the Metaverse as the next-generation computing platform after the mobile internet, saying the Metaverse may also be seen as the Internet with an actual form that can be experienced sensorily.
Tencent CEO Pony Ma said the gate linking the real world to the virtual world is open. Whether it’s constructing the real world based on the virtual world, or mirroring the physical world to the digital world, we are providing ever more real experiences to users.
In fact, it might be difficult to put an academically solid label on what exactly is the Metaverse. After all, all newborn industries would be difficult to define.

In fact, the Metaverse is both real and virtual. It builds a platform that links the real and the virtual worlds. In the real world, people’s lives can go on like normal. On the one hand, the virtual world can copy the fundamental logic of the real world. On the other, the virtual world may also transcend the limitations of time and space, presenting people with wholly new experiences for socializing, entertainment, investment, etc.
In addition, the Metaverse is just like the real world in that besides supporting all forms of activities in the real world, people’s diverse identities, assets, economic systems, cultural customs, laws and regulations can all be reflected in the virtual world. The Metaverse creates a portal to the digital world so that more people can participate.
A Crossroad for the Metaverse
Countless experts have predicted that the Metaverse is the ultimate form of digitalization. It is the upgraded version of the Internet. But there are two problems plaguing today’s version of the Internet.
Security Concerns
A highly centralized Internet is against the ideal of “freedom and openness” advocated in the early days of the Internet. As tech giants control more and more users’ data, they have no restraint at abusing this power to infringe upon user privacy.
If user privacy can’t even be guaranteed in the current stage of the Internet, how are we going to solve this concern after the Metaverse has removed the limitations of time and space?
It’s not difficult to imagine that with the Metaverse bringing the real and the virtual worlds together, users will spend considerably longer time online. Companies facilitating the Metaverse will undoubtedly take the opportunity to peep deeper into user information and monitor their behaviour in the Metaverse.
Without a doubt, the Metaverse will collect personal data in quantities and forms unmatched by today’s Internet. And because of that, the industry should also take on the responsibilities that come with it. To protect data from theft and abuse, the collection, storage and management of data are likely to be put under stronger regulation in the future.
In many countries including China, there are personal data protection laws in place regulating the collection and use of user information. Companies are required to seek user approval before using their personal data. But in reality, it is nearly impossible to give users the ability to track exactly how their data have been used. This task will be even more challenging in the Metaverse.

Computing Power Shortage
The Metaverse will speed up the integration of the real and the digital economy, and the combination of computing power and high-speed internet will lay a solid foundation for the growth of the Metaverse.
Arguably, computing power is the determining factor for how well the virtual world can integrate with our real world.
To build a platform where all types of virtual activities take place, firstly we need to realize that all the content and visual effects in the virtual world are made possible by graphics rendering consuming computing power. Secondly, to give users an immersive and low-latency experience in the Metaverse, we need a high-speed network and the capacity to process astronomical quantities of data, in addition to technologies such as VR/AR, big data, blockchain and AI.
The speed of communication depends on our computing capacity, which determines whether or not we can have a real-world-like low-latency experience. Take Free Guy for example. In the movie, what is happening in the real world can affect the existence of Free City. If computing power was cut off at the end, then Guy wouldn’t have been able to make it past the border of the Free City into the Edenesque world created by Keyboard.

History has proven that computing power will bring about a quantum leap in technologies. Because of this, the demand for computing power in the tech sector is always greater than the supply, especially now with the popularization of the Metaverse, which will remain the largest consumer of computing power so far in human history. Conversely, computing power will also determine the ceiling of the Metaverse.
An unprecedented challenge facing humanity is whether stable and sustainable computing power can be found to support the development of the Metaverse.
As we can see, the issues of privacy protection and insufficient computing power are two obstacles facing the Metaverse, which is now at a crossroads.
For the sustained growth of the Metaverse, we must find the solutions.
1. How to guarantee data security in the Metaverse?
2. How to provide enough computing power for the Metaverse?
3. Are there mature technologies right now that we can apply to the construction of the Metaverse?
How to guarantee data security?
Today, data is becoming an essential factor for all forms of production, and the value of data will only be more pronounced in the Metaverse.
Even though today, the Metaverse is restricted to photos, graphical effects and games, in the future, the Metaverse will integrate the real and the virtual worlds and affect every aspect of our lives. To provide people with a more immersive experience, the Metaverse must first become a gigantic data hub and computing power accelerator.
User data include but are not limited to information about their identity, biometrics, behavioural patterns, social relationship, assets, etc. Even the relationship status and brain wave patterns of users may become useful to collect. The constant updating and production of user private data will be essential for the Metaverse as a fundamental resource as well as a means of production.
For this reason, to protect private data from being illegally collected, stored, managed and used, we must develop tech solutions and regulations to control how data are used. Therefore, privacy-preserving computation will be essential for the Metaverse.
What is privacy-preserving computation?
Privacy Computing: Concept, Connotation and Its Research Trend published in 2016 defined privacy-preserving computation as “a series of theories and methodology governing the full-life-cycle protection of private data, as well as a computable model and axiomatic system facilitating the separation of the right to own, to manage and to use private data, the compensation for data leakage and the assessment of the complexity thereof”.

Privacy-preserving computation is not a standalone technology but rather a system of technologies including cryptology, AI, security hardware, etc. Its purpose is to guarantee the full-life-cycle security of data so that data can be computed and analyzed in a non-transparent way. This way, we can effectively extract value from data, and data can be bought and sold as a resource in the market.
Of these technologies, secure multi-party computation is a branch under cryptology dealing with the protection of data security when a group of non-trusting parties collaborate in a computing task. It guarantees that no single party can know the computing results other than those of the part it is assigned.
While a trusted execution environment (TEE) based on trusted hardware facilitates private data processing and computing as well as the operation of trusted apps. This guarantees that, during execution, data is safe and non-transparent.
In addition, federated learning based on AI is a distributed learning technology integrating cryptology and AI. It aims to protect information and data security during the exchange of big data. This technology is useful for helping industries build machine learning models. Whatever the specific privacy-preserving computation technology, its goal is to make data usable and computable without making them transparent and recognizable.
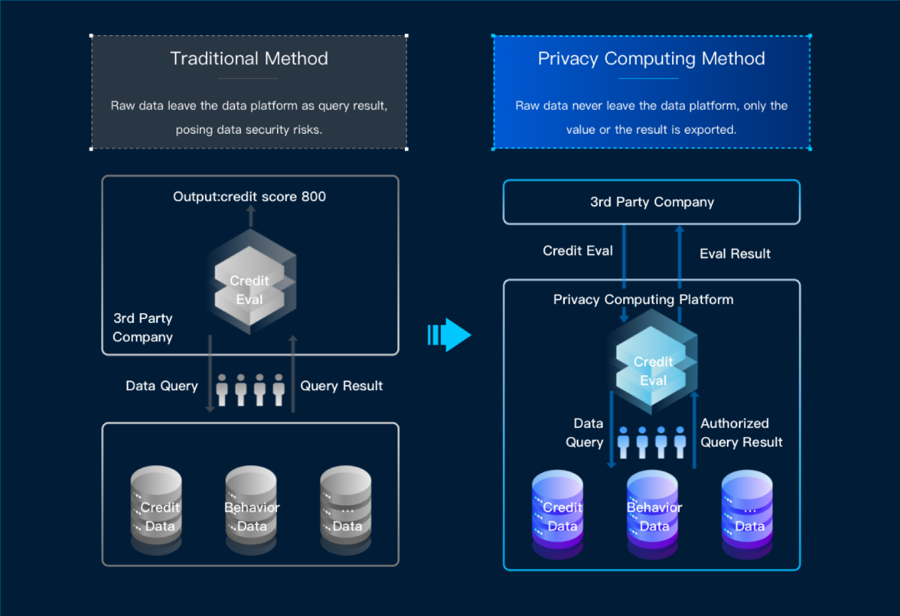
When it comes to application, projects and businesses are constantly trying to integrate blockchain technologies and privacy-preserving computation. On the one hand, data on blockchain need to be protected by privacy-preserving algorithms. On the other, blockchain can serve as a foundation or hub for collaborative privacy-preserving computation tasks.
Thanks to technological advances, blockchain is transitioning from an immutable, traceable and transparent distributed bookkeeping technology into a distributed network data management technology, which utilizes cryptology and distributed consensus protocols for secure data transmission and access so that data can be cross-verified and is globally consistent and immutable.
Although privacy-preserving computation can guarantee the privacy of input data during multi-party collaborative computing tasks, the original data, the computing process, as well as the results, still need to be verified. Thanks to blockchain features such as distributed bookkeeping, smart contract, consensus mechanism, etc, the original data stored on-chain can be authenticated, and the key data and essential steps of computing tasks can be traced back so that the entire process is verifiable.
The full potential of blockchain can only be actualized in combination with practical scenarios and other technologies. Smooth data circulation, the extraction of value from data as well as privacy-preserving computation are perfect areas for blockchain technologies to shine.
Conversely, by applying blockchain’s trusted computing to privacy-computing computation, we can make its process verifiable. The two technologies will add to each other and make for better synergy in data usage on a broader level.
Privacy-preserving computation has already become a practical demand in VR and AR, and it will only be more crucial when building the Metaverse. Through encrypted sharing of private data, privacy-preserving computation offers a solution to ending data abuse on the traditional internet. This way, an endless variety of data can be converted into the fuel for the development of the Metaverse.

How to provide the Metaverse with enough computing power?
Besides data, another type of resource necessary for the well-functioning of the Metaverse is computing power.
Since the Covid-19 outbreak, the digital economy is playing an ever more important role in people’s daily life. People are moving their work, entertainment and socializing online, which fuels the growth of the digital economy. And thanks to the digital economy, people can participate in social activities without leaving home.
As the platform that facilitates all kinds of real-world and virtual activities of humanity in the future, the Metaverse is impossible without advanced computing power infrastructure. Conceivably, the Metaverse won’t be limited to what it’s currently capable of but will fully support an immersive and low-latency experience.
Therefore, to replicate the situations we saw in the movie Free Guy would be rather demanding on our VR/AR hardware technologies, the speed of our network as well as the quality of computing power.
First of all, to enjoy a truly immersive experience, users will need to wear VR/AR/BCI devices, which by that point should become an essential part of people’s daily life just as smartphones are today. In the meantime, the integration between the virtual world and the physical world will create an immersive experience bridging the gap between people’s online and offline lives, which will define the era of the Metaverse.

Low latency involves two aspects. One has to do with people’s Metaverse experience. Real-world and virtual scenes should synchronize with user actions. The other aspect involves guaranteeing the sustainability of computing power. The rate of data communication will grow exponentially, which requires the stable low-latency synchronization and computation of data.
Since the Metaverse is still in its infancy, its growth will depend on the establishment of powerful computing and data storage capacities. To make people’s Metaverse experiences more real and complete, astronomical quantities of data will be produced. The scale and completeness of the Metaverse will be determined by the computing power and storage capacity available in the real world.
As we know, the development of computing capacity will depend on the speed of internet communication as well as the scale of available data. Therefore, computing power and data are interdependent for the success of the Metaverse.
In order to bring the Metaverse into existence and move people’s activities online, the amount of computing power required would be astronomical. Therefore, more and more people are looking towards cloud computing and edge computing for solutions.
Cloud computing is a centralized service where data from all over the world are sent to the cloud for processing. At its core, cloud computing involves gathering together distributed computing resources so that users have limitless access as long as they are connected to the Internet. This also removes the boundary of time and space. According to data from iMedia Research, the global market size of cloud computing is anticipated to reach 265.4 billion USD in 2021.
Whereas, edge computing offers data processing at a physical location close to the source of the data. Its application programs are launched at the edge for swifter internet response. This method offers a solution to the time-critical needs of businesses, practical AI applications as well as security and privacy protection requirements.
As a matter of fact, both cloud computing and edge computing are paradigms of distributed computing capable of improving the speed of the network. Centralized cloud computing services are efficient and secure, and edge computing is responsive and simultaneous. Both deserve to be further explored as computing power solutions for the Metaverse in the future.

Despite their advantages, cloud computing and edge computing have their limits too. Centralized cloud computing exposes user data to risks, while edge computing may be incapable of generating enough computing power for the Metaverse.
Matrix provides computing power for the Metaverse through the separation of computation and consensus.
Even after years of development, there are currently only a small number of projects and businesses engaged in the practical implementation of the Metaverse. And of these, most are only offering watered-down versions that by no means reflect the true potential of the Metaverse and are plagued by numerous technical issues.
For instance, Decentraland, one of the earliest virtual games on Web 3, held a Metaverse meetup last December. During the meetup, the server suffered an overload with merely a few thousand people online so that many players experienced a temporary loss of video and audio signals. In the end, to make the meetup worth it for the attendees, Decentraland had to give in and resort to the centralized Tencent Meeting app instead, which deprived the event of its specialness. This is but one of many such fails.
In fact, gaming and social media are naturally where the Metaverse should gain its first foothold. To develop a game, first, we need to set up the framework of a virtual world so that people can interact and have fun there. With the framework in place, we can introduce an economic system into the game based on the real world. The only challenge here is that, compared to traditional games, network and data exchange latency will be the biggest problem the Metaverse has to solve.
Traditional centralized games support high-frequency interactions between players and the server. Each action players take is synced to the server within tens of milliseconds, which demands much of the upload and download speed of the server.
To decentralize without sacrificing performance sounds like an impossible task, but this is where a technological revolution must take place. Since a decentralized network can theoretically have wide coverage of edge nodes. These nodes can be closer to players than traditional servers, and this way latency can be kept as low as possible. But if so, why are latency still restricting the development and implementation of decentralized blockchains?
To explain this, we need to look at the consensus mechanism of blockchains. Consensus mechanisms are what guarantee the security of blockchains. The programs in the server are calculated and cross-checked by the tens of thousands of nodes in the network. In contrast to the once-and-for-all approach of traditional servers, consensus mechanisms will cause many times more data and computational tasks to flood the network, which makes millisecond-level response speed nearly impossible. Even though players may get assigned a node located closer to them, the benefit of this will be easily outweighed by the extra burden of running consensus algorithms.
With this in mind, if we can find a consensus mechanism that guarantees the security and stability of programs without centralized management, then the mechanism can be deployed onto distributed networks to utilize their computing power resources to the maximum.
This technology is called the separation of computation and consensus. Under this arrangement, consensus algorithms only need to do the thing they are best at doing, while computation will be assigned separately to each node in the decentralized network.
Matrix has designed a wholly new consensus mechanism (Hybrid-PoW) to make this idea come true.
Hybrid-PoW is essentially a marriage of DPoS and PoW. From a mathematical perspective, the long-term expected yields of elective PoW and global full-time PoW are mostly the same, which means the introduction of an election-based mechanism would affect miners much. One challenge, though, is to guarantee the fairness of elections. Most DPoS election mechanisms currently adopted by projects can’t achieve true randomness and fairness. To solve this problem, Matrix has introduced random clustering algorithms (RCA), which categorize nodes by their characteristics and select representatives from them through true random elections.

With the help of RCA, Matrix’s Hybrid-PoW will be more secure, better at guaranteeing fairness and easier to implement. All miners in Matrix AI Network don’t participate in PoW mining in every mining cycle. Only elected miners do PoW computing so that Matrix can export the extra computing power on its platform to clients who need it, just like a cloud computing platform would do.

In a network built on an HPoW consensus structure, users don’t have to go through blockchain to interact with nodes. This avoids latency caused by consensus mechanisms and brings gaming ping down to a millisecond level. Meanwhile, Matrix’s global network of nodes also works as a powerful server to run games on.
In the future, Matrix will open up its entire computing power network so that users can contribute their extra computing power and become a part of the Matrix ecosystem. With good hope, this will become the world’s largest distributed computing power network, and thanks to its support, the full potential of the Metaverse may finally be realized.
MANTA—The Brain of the Metaverse
The Metaverse is essentially a gigantic virtual world where people interact with each other online. Computing power is the foundation of this virtual world, as the rendering of virtual environments and users’ interactions are made possible by computing power. To make the Metaverse truly worthwhile, user privacy must be protected, and the way to do this is through distributed privacy-preserving computation. If the Metaverse were a human, then the computational network would be the brain that commands and provides energy for the whole body.
MANTA of the Matrix ecosystem offers the perfect solution for building such a brain for the Metaverse.
MANTA (MATRIX AI Network Training Assistant) is a distributed auto-machine learning platform built on Matrix’s high-performance blockchain. The platform is essentially an AutoML application together with its deployment system, which uses distributed network technologies for acceleration. The AutoML network searches for a high-precision and low-latency deep model, which is then accelerated through distributed computing. MANTA has two core functions: auto-machine learning (Auto-ML) and distributed machine learning. The framework for the latter is a perfect distributed privacy-preserving computation network.
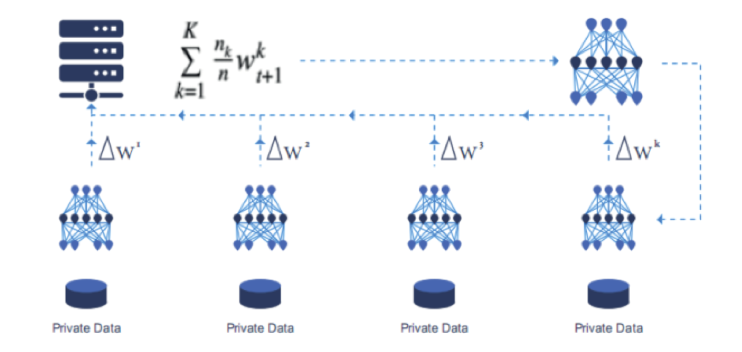
The speed of network searching and training will be further accelerated through distributed GPU parallel computing on MANTA. MANTA’s distributed machine learning is essentially a set of distributed parallel algorithms, which support parallel data and parallel models for acceleration. The idea behind all this is to distribute the data generated in each iteration to different GPUs for forward and backward computing. In each iteration, each GPU will be sampling the same sub-model. Distributed parallel model algorithms are different from parallel data in that, for each iteration, MANTA allows different nodes to sample different sub-networks and conduct a global exchange of gradient information after each node has completed its gradient integration.
Due to the characteristics of MANTA and Matrix’s unique consensus mechanism, this network will be capable of connecting the idle computing power of the world. Your iPad or iPhone could contribute computing power to Matrix while you sleep at night. At the same time, MANTA has a principle of using your own resources to serve yourself first. When your own devices are idle, the system will prioritize using their computing power to support your Metaverse activities. This allows a lower-level privacy strategy to be used to improve efficiency. When using computing power from unknown devices, a higher-level privacy strategy and distributed computing involving more nodes will kick in. We call this smart edge computing, which may eventually prove to be the solution for the huge amounts of privacy-preserving computation necessary for the Metaverse.
Matrix + the Metaverse: A Restructuring of Data and Computing Power
Without a doubt, the Metaverse we are talking about today has far exceeded what the 1992 novel Snow Crash could imagine. In the past decades, we experienced:
· The technological revolution brought about by advances in modern digital information technologies as well as the social and economic changes that followed;
· The social and political environment since the industrial revolution challenged and reforged by the Internet, ushering us into the era of Web 3;
· Advances in VR, AR and MR technologies with ever-growing power to create a virtual world comparable in detail and complexity to our physical world;
· The invention of blockchain, and the new economic possibilities it brought in combination with DeFi, NFT and other financial inventions;
· ……
Looking back, the landmark events in the real history of the Metaverse may be different from what people originally had in mind, whether it’s the level of decentralization, the closeness to reality, customizability, or the maximum number of online users the Metaverse can take. In order to have the Metaverse span all platforms and industries, we must keep looking for creative solutions.
The birth of every new technology in the history of mankind is made inevitable by the technological breakthroughs that preceded it. In essence, the Metaverse is a restructuring of data and computing power. Current limitations are caused by a lack of computing power and effective measures to collect and manage data. The demand for limitless amounts of computing power has given rise to the concept of decentralized privacy-preserving computation.
As far as we can see, the scale of data and computing power will be the single biggest limiting factor for the development of the Metaverse. This challenge will be present at every step in building the Metaverse, and we must find out how to restructure and reassemble data and computing power in order to guarantee user privacy in the midst of the lightning-fast exchange of information. We must also know how to integrate idle computing power from nodes around the globe so they can work seamlessly. These are the focuses of the Matrix team.
We cannot put our finger on by what exact time we’ll gain sufficient and stable computing power to bring the Metaverse to its full potential. But we know that MANTA’s approach to distributed large-scale computing power will play a key role in this, which won’t just benefit the Metaverse, but also be critical for the success of Web 3. The Metaverse is still in its infancy, and Matrix still has a long way to go. But now, as the brain of tomorrow’s Metaverse, MANTA offers us a glimpse of what the Metaverse could be and a future of endless possibilities.
Last updated